Русский | English
Dynamic changes in the gallbladder wall, in the gallbladder bile and in the liver in patients with symptomatic (with biliary pain) biliary diseases
|
|
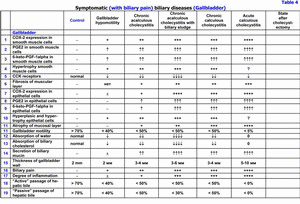
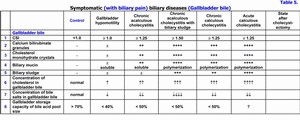
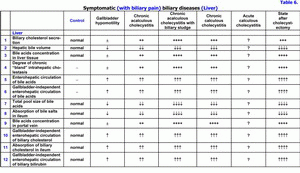
Early detection and the treatment of symptomatic (with biliary pain) biliary diseases have the important clinical importance because of transformation of functional disturbances biliary system into the organic pathology - gallbladder dysfunction → chronic acalculous cholecystitis without biliary sludge → chronic acalculous cholecystitis with biliary sludge → chronic calculous cholecystitis (table 4). It is a result of disturbance of colloidal stability of the gallbladder bile, of precipitation of the cholesterol monohydrate crystals and calcium bilirubinate granules, and the addition of chronic aseptic inflammation in the gallbladder wall (table 5). Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a “gold” standard of the treatment of chronic calculous cholecystitis. The absence of gallbladder promotes the appearance of the functional biliary hypertension and the dilation of the common hepatic duct and common bile duct. In some patients it is accompanied with progressive deterioration of the chronic pancreatitis, with appearance of dysfunction of Oddi's sphincter, of duodeno-gastral reflux and/or of reactive hepatitis (table 6). Possibly, the symptomatic (with biliary pain) biliary diseases are the “COX-2” associated biliary diseases. The main cause of these diseases is the excessive COX-2 expression in the smooth muscle cells and in the epithelial cells of the gallbladder and of the common hepatic duct and common bile duct. Probably, the symptomatic (with biliary pain) biliary diseases are the diseases of the smooth muscle cells of the gallbladder wall or of the smooth muscle cells of cystic duct, of the common bile duct sphincter or of the pancreatic duct sphincter or of the sphincter of ampulla (the excessive COX-2 expression).
|
|
|